Operators & Expression
- Operators and its types
-
- Arithmetic Operators
-
- Unary
- Binary
- Ternary
- Comparison and Logical Operators
- Assignment Operators
- Bitwise Operators
- Others
- Operators precedence and associativity
Assignment Set
- List all the operators with their type, precedence & associativity.
- What is modulus operator? What are the restrictions of a modulus operator?
Board Exam Theory Questions
- Describe the meaning of precedence and associatively of operators with example. How much memory is required for long integer and its range? [2+4] [Board]
- What is operator? Describe the conditional operator in C with syntax and example. [2+3][2073]
- What are the differences between global and local function, variables and data types, & (Ampersand) operator and * operators used in c-programming language? Explain with example. [4+4]
- What do you mean by precedence and associativity of an operator? Explain with suitable example. [3] [2072]
- What is an operator, data type, constant and variable? Define. [6] [2072]
- What are relational operators and assignment operators? Explain with examples. [3] [2070]
- What are unary operators in C? Why are they named so? [2] [2068]
- Explain the operators available in C along with their precedence and associativity. [4] [2067]
- Explain with an example the role that precedence and associativity play in the execution of an expression. [4] [2074]
Operators
Operators are the symbol that tells the computer to perform certain mathematical and logical operation. And the data item or value on which operator perform the certain operation is called operand.
Classification
- Arithmetic operator
- Relational operator
- Logical operator
- Assignment operator
- Conditional operator
- Bitwise operator
1. Arithmatic operator
The arithmetic operator perform arithmatic operation. It can be classified into Unary & Binary operator.a) Unary operator
The operator which required single operand for operation is known as unary operator. Example:| Unary Operator | Purpose |
|---|---|
| a++ | (increment operator) final value a+1 |
| a-- | (decrement operator) final value a-1 |
| -p | (Unary minus) positive p change to -ve i.e. -p |
b) Binary operator
The operator which required two operand for operation is known as binary operator. Example:| Binary operator | Purpose |
|---|---|
| + | Addition (a+b) |
| - | Subtraction (a-b) |
| * | Multiplication (a*b) |
| / | Division (a/b) |
| % | Modulus (a%b) |
2. Relational Operator
The relational operators are the symbols which is used to compared two or more subject matter. Example:| Relational operator | Purpose |
|---|---|
| << /td> | (smaller than) a < 5 |
| > | (greater than) a > 5 |
| <=< /td> | (smaller than equal to) a <= 5 |
| >= | (greater than equal to) a >= 5 |
| == | (equal to) marks == 32 |
| != | (not equal to) mark != 32 |
3. Logical Operator
The logical operator are used to combine two or more than two expression of relational operator. Example:| Logical operator | Purpose |
|---|---|
| && | (and) if(age>50 && salary>5000) |
| || | (or) if(age<50 || age>20) |
| ! | (not) mark != 32 |
4. Assignment Operator
Assignment operator are used to assigne a value of right hand variable to left hand variable.Example:
A = l x b
sum = a + b
Difference between:
| Assignment operator (=) | Equality operator (==) |
|---|---|
| Assignment operators is used to assign a value to a variable. | Equality operator is used to determine if two expression have the same value or not. |
5. Conditional Operator (Ternary Operator)
The conditional operator consists of two symbols and three expression. The symbols are (?) and colon (:). The conditional expression is written asExpression1 ? Expression2 : Expression3
Here, Expression1 is evaluated first. If it is true, then Expression2 is evaluated else Expression3 is evaluated. This is also called short cut version of if else statement. Example:
a>b ? a-b : a+b
Here, if a is greater than b then Expression2 is evaluated else Expression3 is evaluated.
6. Bitwise Operator
A bitwise operator operates on each bit of data. Usually bitwise operators are not useful in cases of float and double variable.| Operators | Symbol | Working function | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bitwise AND | & | If both ON then ON else OFF | 100 & 101 = 100 |
| Bitwise OR | | | If any one ON then ON else OFF | 100 | 101 = 101 |
| Bitwise XOR (Exclusive OR) | ^ | If both ON or OFF then OFF else ON | 100 ^ 101 = 001 |
| Left shift | <<< /td> | Indicates the bits are to be shifted to the left | 1111<<2=> 1100 |
| Right shift | >> | Indicates the bits are to be shifted to the right. | 1111>>2 => 0011 |
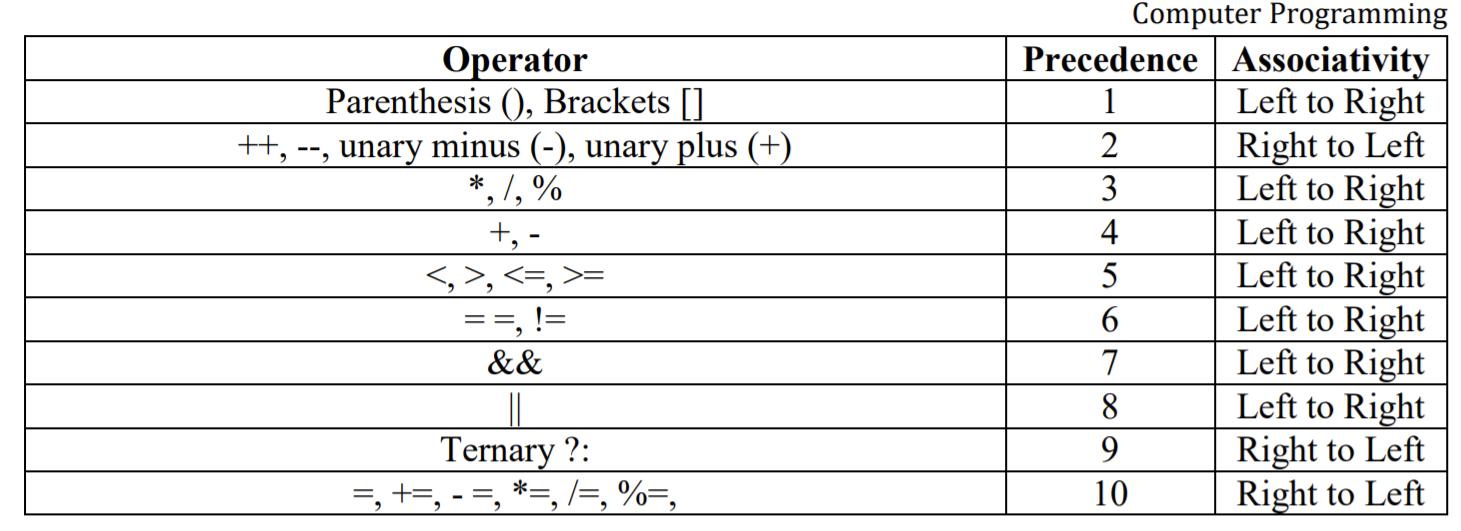
Precedence & Associativity
Precedence
In a statement consisting of multiple operators, the criteria or rules that determine which operator should be operated or carried out first is called precedence of an operator.Consider the following two statement
int a = 1, b = 2, c = 3, d;
d = a + b * c;
Here, b is multiplied by c first. The result is added to a and the sum is assigned to d. Since multiplication is done before addition the multiplication operator has a highest precedence than the addition one.
Associativity
If an expression contain two or more than two operator which have same precedence then priority is evaluated either from left to right or from right to left. This is known as as associativity.For example in the expression
d = a - b - c ;
The first (left-most) minus is evaluated first. The variable is subtracted from a. Then the second minus is evaluated, causing c to be subtracted from the result.
Programming Set
- Write a program to convert centigrade to Fahrenheit. [F = 9/5 * C + 32]
- Write a program that calculates the area of a circle and circumference.
- Write a program that calculates the area of a triangle.
- Write a program that reads the marks in each subject and calculates the percentage.
OPERATORS
Arithemetic Operator
- What will be the output of following
program?
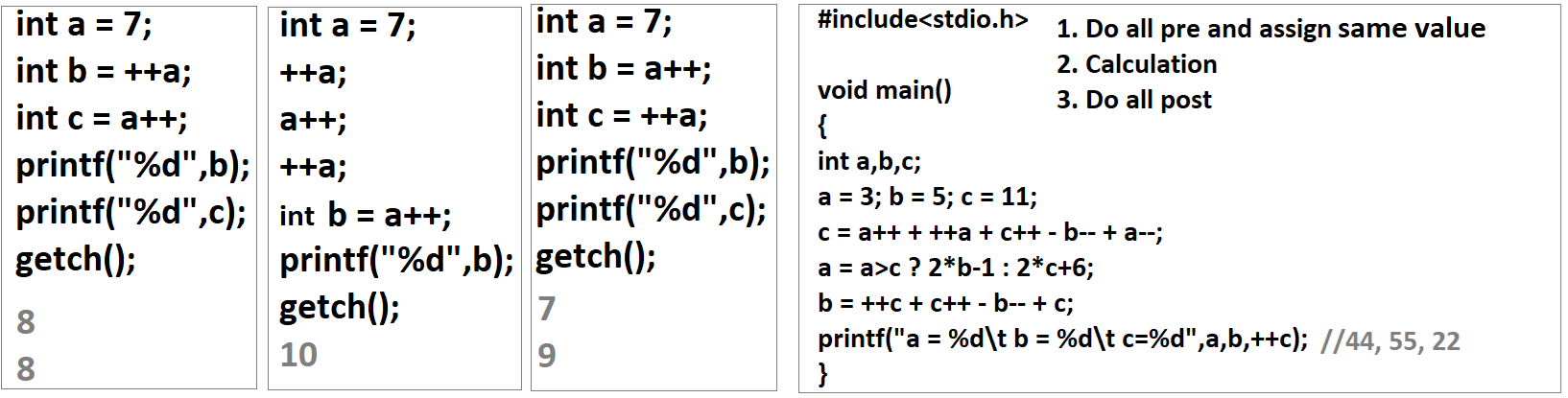
- WAP to add two numbers given by user.
- WAP to enter a no. and check whether it is even or odd.
Relational Operator
- WAP to enter numbers and check whether they are exactly equal or not.
- WAP to find a larger number among two numbers.
Logical Operator
- WAP to enter three no. and display the largest number.
- Any character is entered through the keyboard. WAP to determine whether the character entered is capital letter, a small letter, a digits or special symbols.
Assignment Operator
Conditional Operator / Ternary Operator
- WAP to enter two numbers and display the largest number using ternary operator.
- WAP to enter two numbers. Make comparison between them with conditional operator. If the first number is greater perform subtraction otherwise addition.