Functions
- Function Concepts
-
- Declaration of Function
- Defining Function
- Calling Function
- Types of Function
-
- Built-in-function
- User-Defined function
-
- No-Return type with No-Arguments
- Return type with No-Arguments
- No-Return type with Arguments
- Return type with Arguments
- Calling a function
-
- Call-by-value
- Call-by-reference
- Passing a function
-
- Pass-by-value
- Pass-by-reference
- Arguments in Function
- Return Statements
- Passing Multiple arguments to a function
- Advantages of using function
- Recursion
- Recursive function
Assignment Set
- What are the different types of functions available in C program? Explain in detail.
- Differentiate between function declaration and definition.
- What is the main limitation of return statement & how can we overcome this?
- What is a recursive function? What are its requirements? Explain with an example.
- Compare Iteration with Recursion.
- Explain Call-by-value and Call-by-reference approach of calling a function with suitable example.
Board Exam Theory Questions
- When can we use recursive functions? [2] [2074]
- What are the advantages of using functions? Differentiate between Library functions and User-defined functions with suitable example. [5] [2073]
- Differentiate between pass by value and pass by reference. [3] [2073]
- Explain the significance of user defined functions with example. [5] [2073]
- What is the meaning of function prototyping? [2] [2072]
- Briefly explain the passing by value and passing by reference in function with example. [6] [2072]
- What is recursive function? How does it work? [2+2] [2071]
- What do you mean by nested function and recursive function? [2]
- Give an example of recursive function. [2]
- Define “function definition” and write the program to find the sum of two numbers using user-defined functions. [4] [2070]
- What do you mean by “call by value and call by reference” along with suitable example? [4] [2070]
- Explain how function is defined in C? Differentiate call by value and call by reference. [1+2] [2070]
- What is a function? Why is it necessary in programming? [1+2] [2069]
- Write down significance of main() function in C. Differentiate between pass by value and pass by reference arguments. Describe both with meaningful example. [2+6] [2069]
- Why programmers prefer using user defined functions? What is merits and demerits of using functions in program? Differentiate actual and formal parameters used in functions? [3+2+3] [2068]
- How recursion is different from iteration? [1]
- Write a syntax of static. [2] [2067]
- Distinguish between call by value and call by reference with example in C. [2] [Board]
- Classify the variable according to the scope and extent (storage class) with C. [2] [Board]
- State with example, how switch() function differs from user defined function in computer programming language C. [4] [067]
- How can you differentiate between ‘called by value’ and ‘called by reference’ with example in C programming? [6] [067]
Function
A function is a block of code that performs a specific task.Or a number of statement grouped into a single logical unit is called function.
C program may contain two or more than two function. Among these function any one of them must be the main function which is executed at the beginning and other function is executed when main function called them.
A function can also be referred as a method or a sub-routine or a procedure, etc.
Two types of function
- Library function
- User defined function
| Library Function | User defined Function |
|---|---|
| These function are predefined in the compiler of C language. | These functions are not predefined in the Compiler. |
| The function which are already written by the C-languages developer is library function. | The function which are written by the programmer at the time of writting program. |
| The programmer can only use these function. These cannot be modify. | These function can be modify by the programmer. |
| There are many library function of different types. |
User defined function are of only four types. - without return type without argument (0,0) - without return type with argument (0,1) - with return type without argument (1,0) - with return type with argument (1,1) |
| Library function requires a header file to use it. | User defined function requires a function prototype to use it. |
| Program development time will be faster. | Program development time will be usually slower. |
| E.g. printf(), scanf(), getch(), scanf(), pow(). | E.g. addition(), fact()...etc. |
In order to make use of user defined function we need to established 3 main elements. The three main elements are:
- Function declaration (Function prototype)
- Function call (Calling function)
- Function definition (Called function)
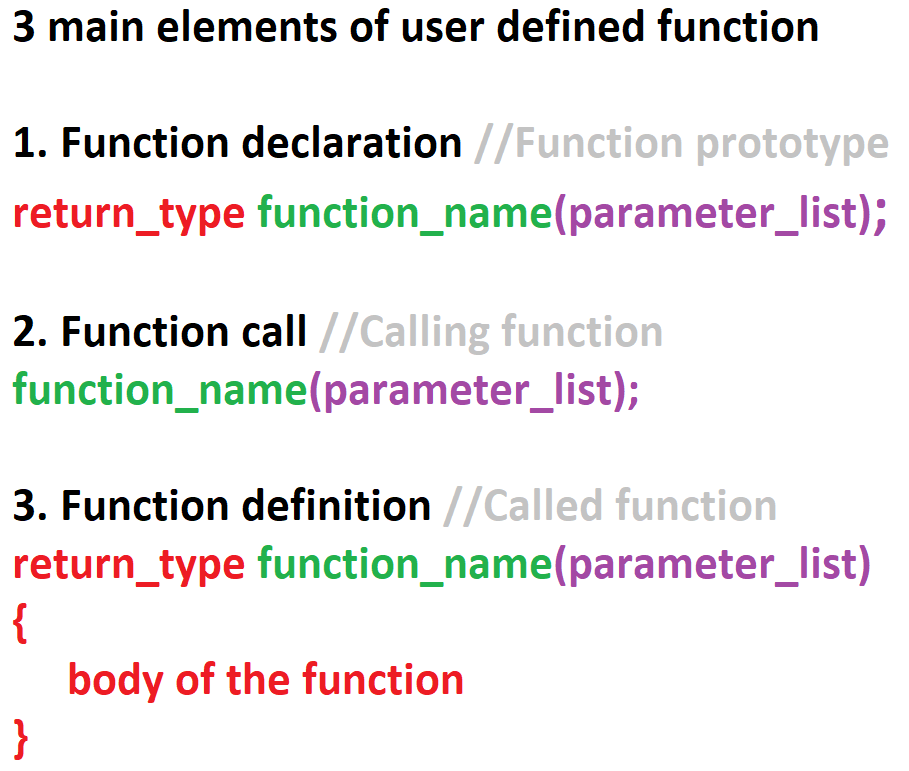
1. Function declarations
A function declaration tells the compiler about a function name and how to call the function. The actual body of the function is defined separately.A function declaration has the following parts:

Parameter names are not important in function declaration only their type is required, so following is also a valid declaraction.

2. Function call
While creating a C function, you give a definition of what the function has to do. To use a function, you will have to call that function to perform the defined task.
When a program calls a function, the program control is transferred to the called function. A called function performs a defined task and when its return statement is executed or when its function-ending closing brace is reached, it returns the program control back to the main program.
To call a function, you simply need to pass the required parameters along with the function name, and if the function returns a value, then you can store the returned value.

3. Function Definition
The general form of a function definition in C programming language is as follow:
A function definition in C programming consists of :
- Return Type: A function may return a value. The return_type is the data type of the value the function return. Some functions perform the desired operations without returning a value. In this case, the return_type is the keyword int.
- Function Name: This is the actual name of the function. The function name and the parameter list together constitute the function signature.
- Parameters: When a function called, you pass a value to the parameter. This value is referred to as actual parameter or argument. The parameter list refers to the type, order, and number of the parameters of a function. Parameters are optional; that is, a function may contain no parameters.
- Function Body: The function body contains a collection of statements that define what the function does.
-
Return statement: Return statement is used in the called function in order
to return value to the calling function. A return statement return only one value at
a time. In order to return more than one value we use call by reference without
using return statement.

Types of User define function
- With no return type with no argument (0,0)
- With no return type with argument (0,1)
- With return type with no argument (1,0)
- With return type with argument (1,1)
Two method of passing argument
- Call by Value
- Call by reference
| Call by Value | Call by Reference |
|---|---|
| The process of passing values of the variable from the calling function to the called function is call by value. | The process of passing memory address of variable form calling function to the called function is call by reference. |
| Any change made to the formal argument does not affect actual argument. | Any change made to formal argument affects the actual argument. |
| Pointers are not used to pass the value. | Pointers are used to pass the address. |
| In call by value only one value can be return at a time. | In call by reference more than one value can be return at a time. |
| Return statement is used to return the value. | Return statement is not used to return multiple value. |
Storage class
In order to define a variable completly we need to mention not only its data type and name but also its storage class.The storage class gives the information about
- initial value of the variable i.e. if we do not explicitly initialize that variable, what will be its default initial value.
- the part of the memory where the variable would be stored
- scope of variable i.e. where the value of the variable would be available inside a program.
- lifetime of variable i.e. for how long will that variable exit.
- Local or automatic storage class
- Global or external storage class
- Static storage class
- Register storage class
Local (Automatic) variable
The variable declared inside a particular area or block is called local variable. And the keyword for local or automatic variable is auto.Declaration:

- Initial Value: Garbage value i.e. Random value
- Storage space: temporary memory (RAM)
- Scope/Visibility: Within the block where it is declared. (local)
- Lifetime: Till the control remain within that block
Global (External) variable
The variable declared outside the main function and which is active and alive as long as the program execution does not come to an end. And the keyword for global variable is extern.Declaration:

Note: If the global and local variable is declared with same name then priority is given to local.
- Initial Value: Zero
- Storage space: temporary memory (RAM)
- Scope/Visibility: Global i.e. everywhere in the program, Multiple files
- Lifetime: as long as program execution does not come to an end.
Static variable
The variable whose value is not destoryed on exit and become available again when the function is next called. And the keyword is static.Declaration:

The variable may be local or global.
- Initial Value: Zero
- Storage space: temporary memory (RAM)
- Scope/Visibility: Value of variable persists between different function call.
- Lifetime: if local: lifetime is within that bloc, if global: lifetime is for whole program.
Register variable
Register variable inform the compiler to store the variable in CPU register instead of memory. Register variables have faster accessibility than a normal variable. Generally, the frequently used variable are kept in registers. But only a few variable can be placed inside registers. One application of register storage class can be in using loops, where the variable gets used a number of times in the program, in a very short span of time.Declaration:

Note: We can never get the address of such variable.
- Initial Value: Any random value i.e. garbage value
- Storage space: CPU register
- Scope/Visibility: Local to the function in which it is declared.
- Lifetime: Till the end of function, in which the variable is defined.
Recursive Function
In C programming, a function is allowed to call itself. And a function which calls itself again and again until some specified condition is satisfied is known as Recursive Function.Advantages of function and recursive function
- Function helps in easy understanding, debugging and testing of the program.
- Function reduces size, length and complexity of program.
- Function save time by avoiding repeatation of same code.
- Distributing of work is possible due to function.
- Motivates the programmer to built new powerful program.
Programming Set
- Write a program to identify whether the given number is a perfect number or not using a function. 28 is a perfect number.
- Write a program to evaluate GCD of two given integers. Use function that returns GCD.
- Write a recursive program to find the factorial of a given number.
- Write a recursive program to find a GCD of two numbers.
- Write a recursive program to find the sum of n natural numbers.
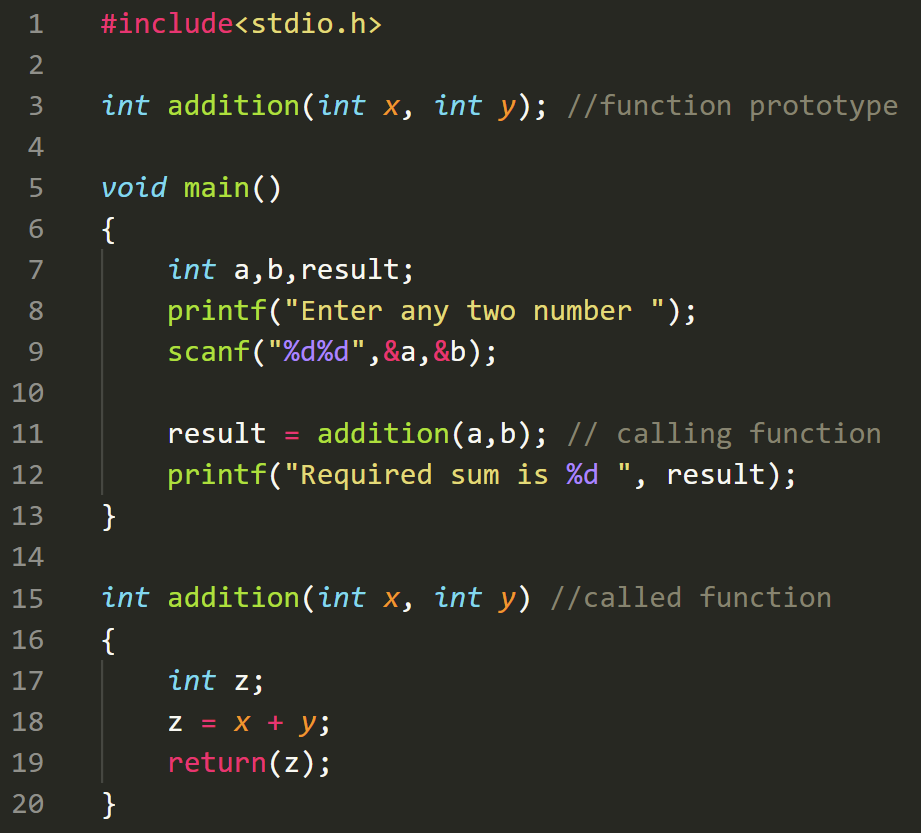
USER DEFINED FUNCTION
- WAP to add two numbers using function.
- WAP to enter a number in main function, passed it into user define function, find the factorial and print it in main.
- WAP to compute
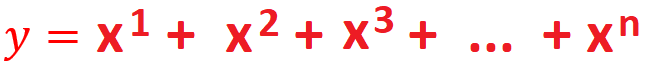 without
using power function.
without
using power function. - WAP to find
the series
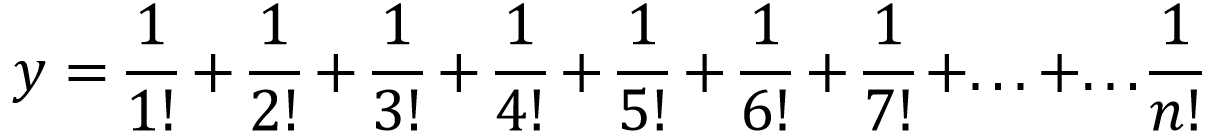 .Use function to calculate the factorial.
.Use function to calculate the factorial. - WAP to
calculate the value of an expression
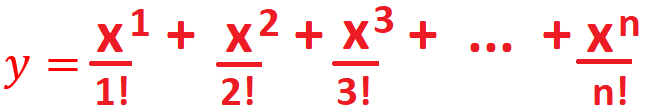 .Use function to calculate the
factorial.
.Use function to calculate the
factorial. - In pass by value, any change made to formal argument does not affect actual argument.
- In, pass by reference, any change made to formal argument affects the actual argument.
- WAP showing how we can return more than one value.
- Write a program to find whether a number is prime or not using function. The function should take the number as argument and return true or false to the main program. [5] [069]
- Write a program in C to find out whether the nth term of the Fibonacci series is a prime number or not. Read the value of n from the user and display the result in the main function. Use separate user-defined functions to generate the nth Fibonacci term and to check whether a number is prime or not. [8] [074]
- WAP to convert list of temperatures in Centigrade to Fahrenheit with necessary comments using user defined function. [4] [069]
- WAP to read two integers from the user. Pass it to functions that calculates the HCF and LCM. Display the result from the main function. [5] [066]
RECURSIVE FUNCTION
- WAP to enter a number and find the factorial of a number using recursive function.
- WAP to enter a number and find the sum of the series using recursive function. 1+2+3+4+5+...+...n
- WAP to display a line of text “Programming is fun” 5 times using recursive function. [058]
- WAP to display a line of text “AAMIR KHAN Mr. Perfectionist” n times as the user specifies using recursion. [Extra]
- WAP to find the Fibonacci series up to N terms given by user using recursive function.
- Write a program to check whether a given number is Armstrong number (3 digits) or not using recursive function. [5] [073]
- Write a program to calculate the sum of the series 1+11+111+....+ up to N terms using recursive function. If N is read as 5, the series is: 1+11+111+1111+11111. [6] [072]
- Write a program to calculate sum of digits of a given 5-digits number entered by the user using recursive function. [4] [072]
- Find out sum of digit of number until the number becomes one digit number using recursive function. [891>18>9] [4] [071]
- WAP to check whether the number is power of 2 or not using recursion.
- WAP to print the HCF of two numbers given by user using recursive function.
- WAP using recursive
function to compute series:
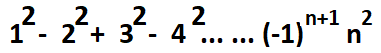 Here, you cannot use pow() function, where
n is taken from user.
Here, you cannot use pow() function, where
n is taken from user. - WAP to find the sum of following series. 12-22+32-42+52-62+….using recursive function.
- WAP to find the
sum of the following series,
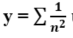 up to n terms using recursion. [064]
up to n terms using recursion. [064] - WAP to find the sum of numbers till the user enters non-negative integer numbers using a recursive function. [064]